Restriction Analysis
In this chapter, you will learn how to search for restriction sites in a DNA sequence.
The restriction sites found are stored as automatic annotations. This means that if the automatic annotation highlighting is enabled, then the restriction sites are searched for and highlighted for each nucleotide sequence opened. Refer to Automatic Annotations Highlighting to learn more.
Open a DNA sequence and click the following button on the Sequence View toolbar:

The Find restriction sites dialog appears:
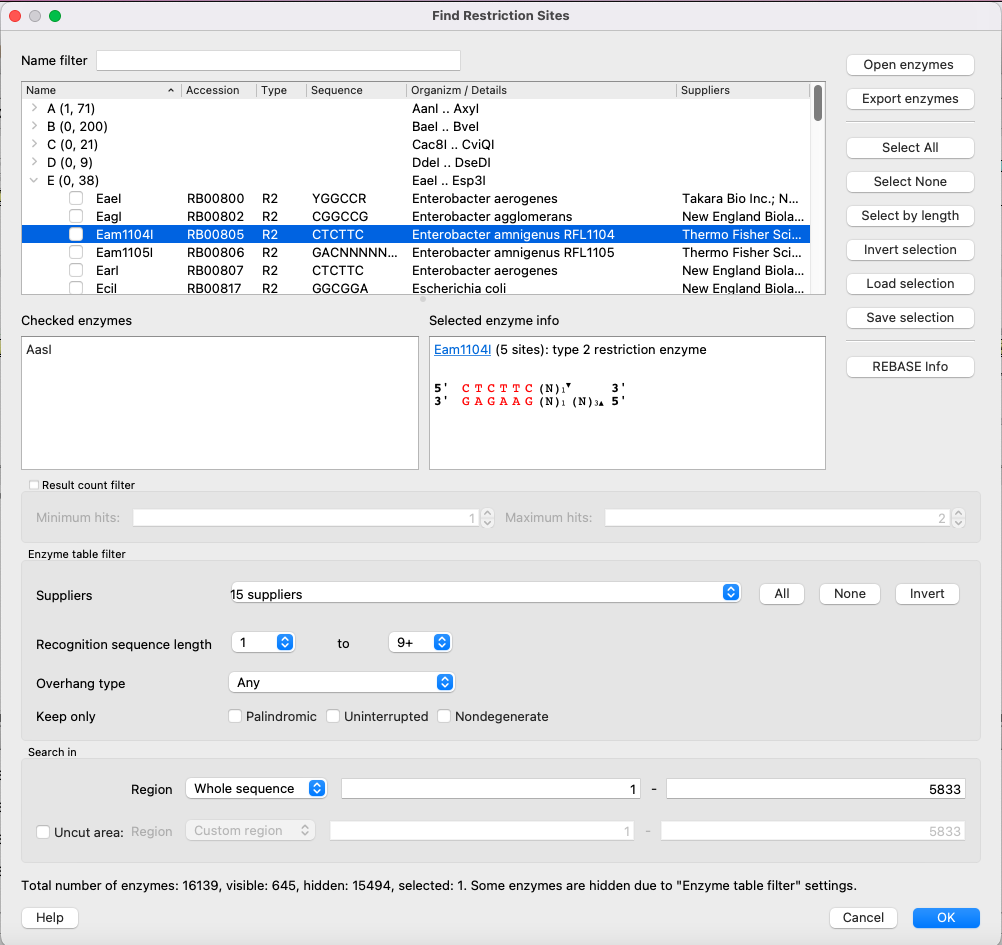
The Tree of Restriction Enzymes
Restriction enzymes are collected in a tree view. Enzymes are grouped by the first letter of their names. Click on the > icon of a group (or just double-click on the entire line) to show the whole group. Check the checkbox to include an enzyme in the search list and uncheck it to exclude it. Use the Name filter to find a certain enzyme by its name.
Checked Enzymes
Here you can see all the checked enzymes. These enzymes will be searched for after clicking OK.
Selected Enzyme Info
Some information about the selected enzyme is provided. It includes the name, a link to the REBASE database, detailed information about the enzyme type, the number of enzymes in the current sequence, and sites and cut locations.
Control Buttons (Right Side)
- Open enzymes - open a file with enzymes in the Bairoch format. This is required if you want to update the enzyme database or open a database with a limited amount of enzymes. See Using Custom File with Enzymes for details.
- Export enzymes - export selected enzymes to a separate file (using the Bairoch format).
- Select all - check all enzymes in the tree.
- Select none - uncheck all enzymes in the tree.
- Select by length - check enzymes only if their recognition site has a length greater than you set in the dialog window that appears.
- Invert selection - switch checked and unchecked enzymes.
- Load selection - load selected enzymes from the file. This file should contain a comma-separated enzyme name list, for example: BamHI,BglII,ClaI,DraI,EcoRI,EcoRV,HindIII,PstI,SalI,SmaI,XmaI.
- Save selection - save checked enzymes to a separate file using the format described above.
- REBASE info - open the REBASE database page of the selected enzyme.
The Filter of the Results Number
Show an enzyme only if there are at least the “Minimum hints” value and at most the “Maximum hints” value.
Enzyme Table Filter
Show/hide enzymes depending on certain parameters:
Suppliers - check/uncheck suppliers whose enzymes will be shown. By default, enzymes with undefined commercial suppliers are not shown.
Recognition sequence length - show only enzymes whose recognition sequence length is within bounds. NOTE: N bases are not included in the recognition site. That means that if an enzyme has the following sequence:
C C N N N N N N N G Gits recognition site length will be four, not eleven.
Overhang type - show only enzymes with a certain overhang type. The following options are presented:
Any - show all enzymes.
No overhang - the site has no cuts at all.
3' CTCGAG 5' 5' GAGCTC 3'5’ - the cut of the forward strand is to the left of the cut of the reverse-complementary strand.
3' C C▼T N A G G 5' 5' G G A N T▲C C 3'3’ - the cut of the forward strand is to the right of the cut of the reverse-complementary strand.
3' C G A T▼C G 5' 5' G C▲T A G C 3'Blunt - cuts are located in the middle of the site.
Sticky - cuts are located anywhere but the middle of the site. It includes both 5’ and 3'.
Nondegenerate sticky - the same as Sticky, but the overhang between cuts has only A, C, G, or T (no extended) symbols.
Blunt or sticky - Blunt + Sticky.
Blunt or nondegenerate sticky - Blunt + Nondegenerate sticky.
Keep only - show the most interesting enzymes only:
- Palindromic - forward and reverse-complementary strands are equal.
- Uninterrupted - no internal N bases.
- Nondegenerate - no extended DNA alphabet symbols (only A, C, G, T, and N).
Search Region
The region to search enzymes in. If you check the Uncut area checkbox, then restriction enzymes, which exist outside of the uncut area but also persist inside of it, won’t be included in the result.
Example:
You will find two “AsaI” enzymes in the following sequence if you choose the whole sequence as Search in:

But, if you also set the Uncut area to 60-90, you will not find any enzymes at all and will see the following sign in the log: The following enzymes were found but skipped because they are presented inside of the “Uncut area”: AsaI.
The information about enzymes was obtained from the REBASE database. For each enzyme in the list, a brief description is available (the accession ID in the database, the recognition sequence, etc.). If you’re online, you can get more detailed information about a selected enzyme by clicking the REBASE Info button.