Running Workflow from the Command Line
UGENE provides a command-line interface (CLI). To learn more about the UGENE CLI and the available commands, read the main UGENE User Manual.
This chapter describes how you can create a new command using a workflow.
To run a workflow from the command line, do the following:
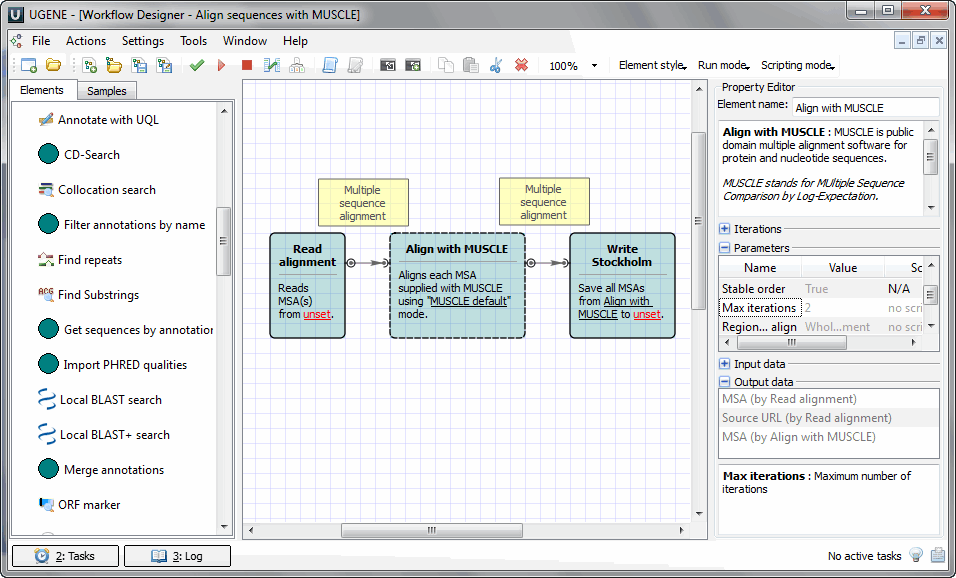
- Create the workflow in the Workflow Designer. For example, in the image below, the Align sequences with MUSCLE sample workflow is used:
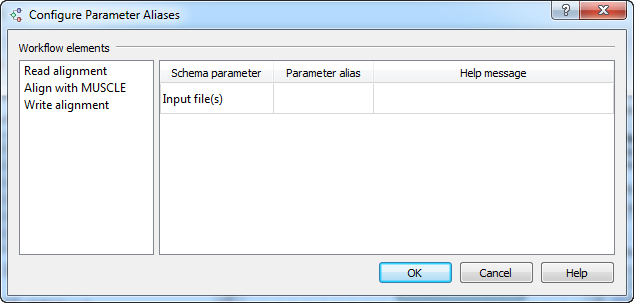
- Now you should configure aliases for those parameters, ports, and slots that you are going to use from the command line. To do this, select the Actions ‣ Set parameter aliases… item in the main menu or click the Set parameter aliases toolbar button. The following dialog appears:
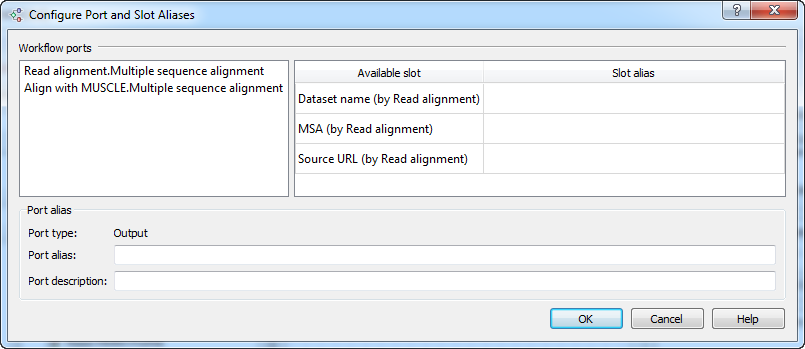
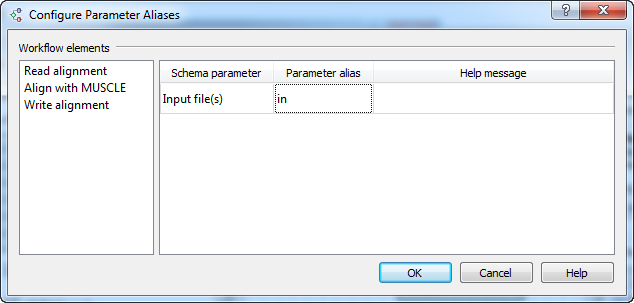
It contains the list of objects that correspond to the elements of the workflow. For each object, a list of parameters is available for which you can assign command-line aliases. For example, assign the alias in to the parameter Input file (of the Read alignment element):
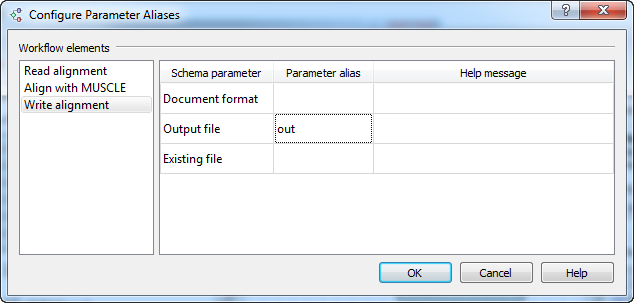
And assign the alias out to the parameter Output file (of the Write Stockholm element).
To select ports and slots aliases, use the following dialog by the Actions->Configure port and slot aliases main menu item:
Press the Ok button to save aliases and close the dialog. When you create aliases, you can import the workflow to an element using the Actions->Import workflow to element main menu item.
- Save the workflow to a file: If you follow the example, choose the Actions ‣ Save workflow as… item in the main menu, browse for the file location, and enter mySchema as the workflow name. This name will be used to launch the workflow from the command line.
- Launch the workflow from the command line:
[path_to_ugene]ugene --task={schema_name} [--{parameter1}={value1} [--{parameter2}={value2} ...]]
The run information will be saved into the text file. By default, it is in the working directory.
For example, on Windows, the command can look as follows:
ugene --task=C:\mySchema --in=C:\COI.aln --out=C:\COI.sto
In this example, the path to the directory with the UGENE executable is added to the system PATH variable.