Tutorial: Metagenomic Classification with Kraken
In this tutorial we will learn how to classify our metagenomic reads obtained with Illumina sequencing platform with Kraken, a system for assigning taxonomic labels to short DNA sequences.
You can find more information about Kraken here:
- Kraken website: https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/kraken/
- Kraken manual: http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/kraken/MANUAL.html
We have collected field mosquitoes from different locations across Florida, United States, and we want to understand what is the composition of their microbiome. We have extracted RNA and performed shotgun sequencing with Illumina. The reads are 2x150bp paired-end reads. Here we will analyze one of the sites.
We have two datasets, lib3 and lib5. Let’s start with lib3.
This is the workflow that we will follow:
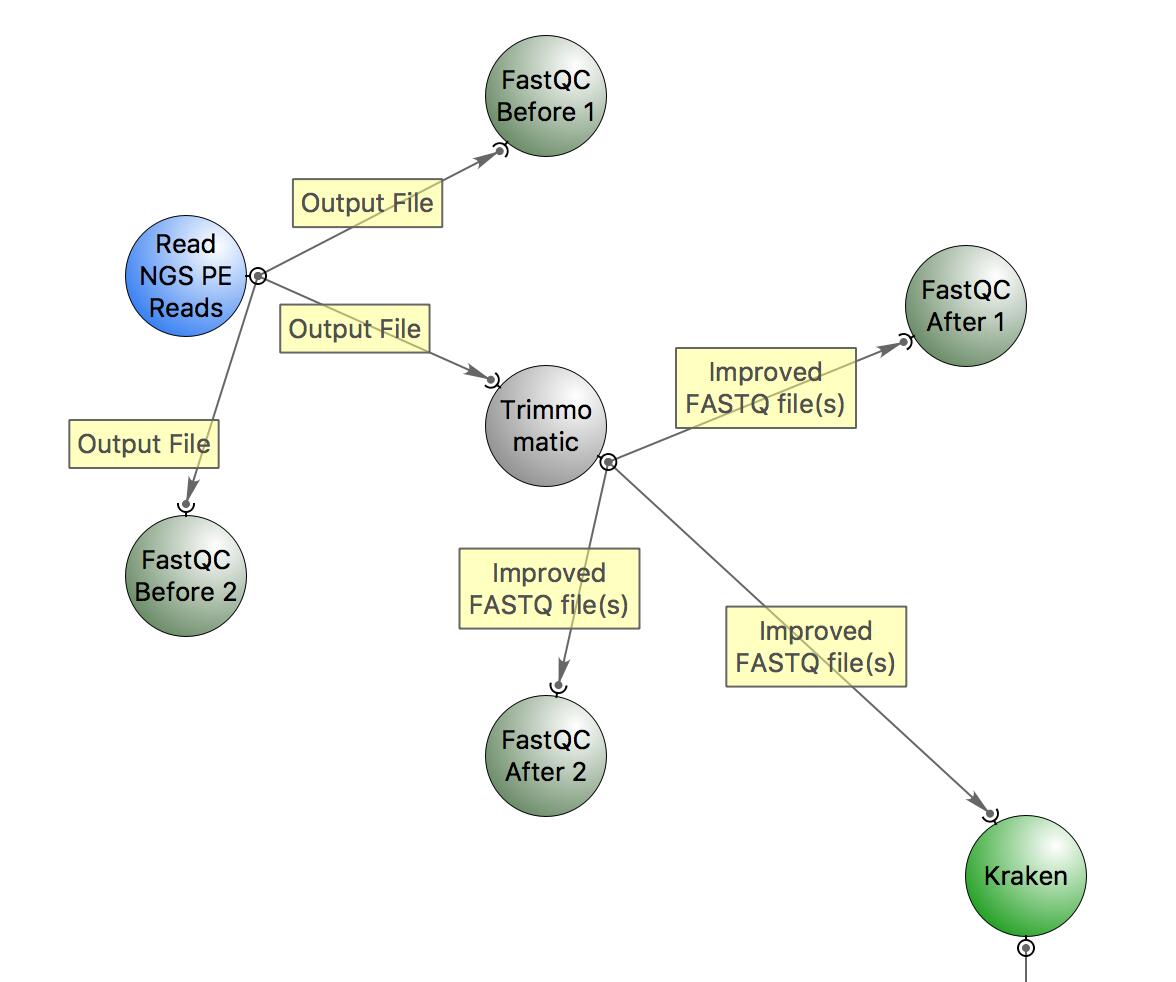
The workflow includes:
- quality check with FastQC,
- trimming with Trimmomatic,
- classification of reads with Kraken.
System requirements
To follow this tutorial you need to have:
- Operating system: 64-bit Linux or macOS
- RAM: at least 8 Gb
- Disk space: about 50 Gb of free disk space is required
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 1.8 or higher should be installed.
- To use the UGENE online installer (see below) you need to have administrative rights on the computer.
UGENE configuration
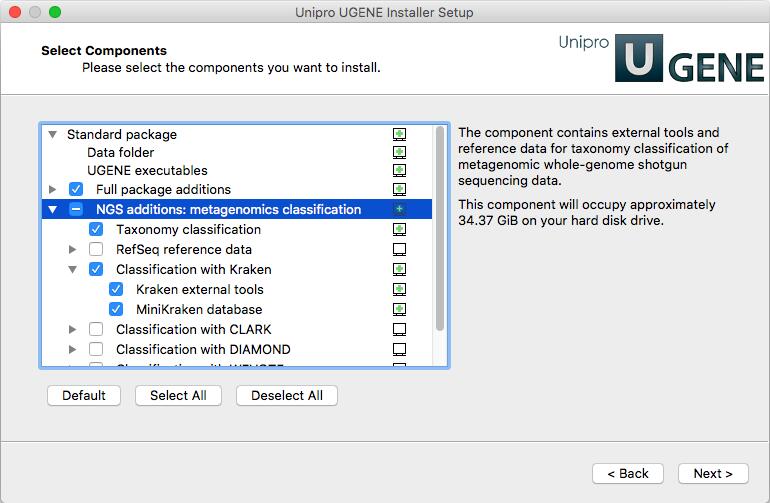
Download the UGENE online installer (version 1.31 or higher is required) and install it (see instructions for Linux and macOS). On the “Select Components” page select “Taxonomy classification” and “Classification with Kraken” items under “NGS additions: metagenomics classification”.
Sample data
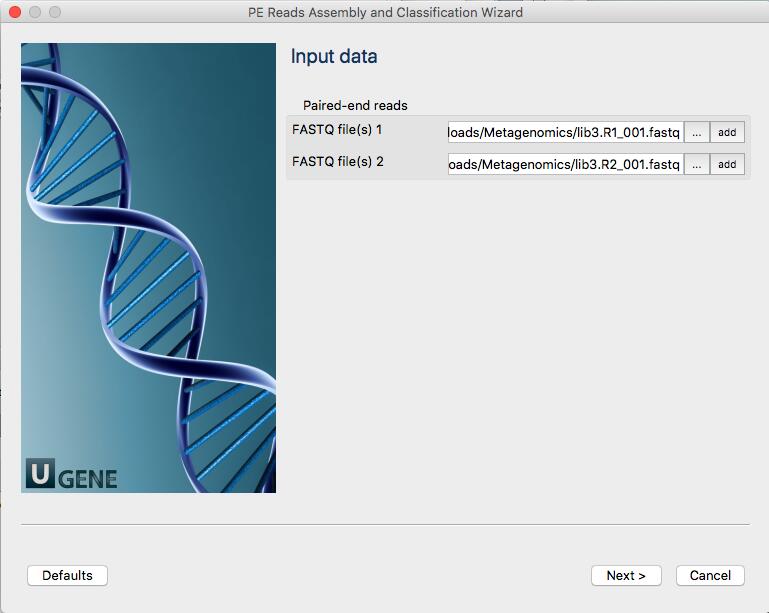
Download files “lib3.R1_001.fastq.gz” and “lib3.R2_001.fastq.gz” from here and unpack each file.
Tutorial steps
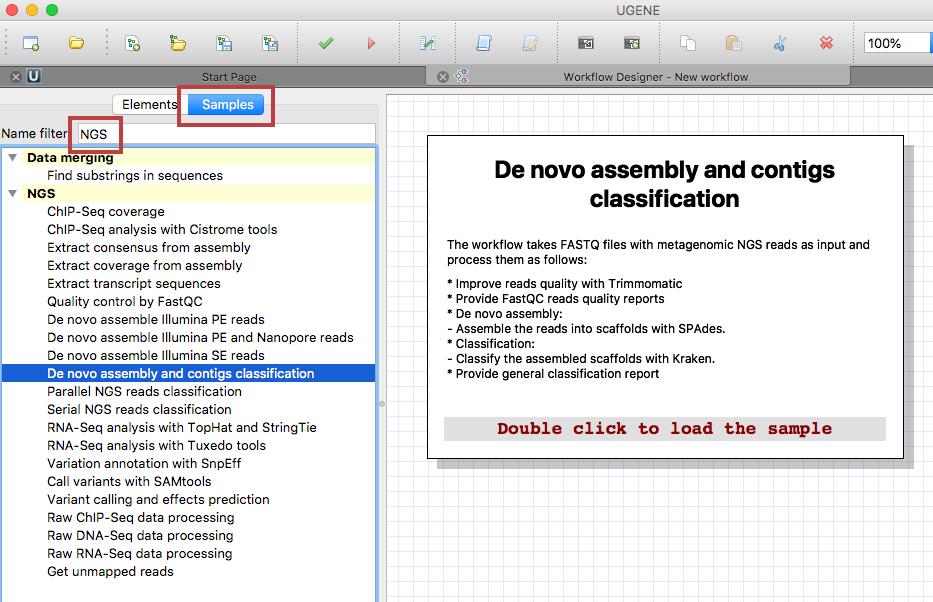
Select “Tools > Workflow Designer” in the UGENE main menu. In the appeared window search for NGS under the “Samples” tab and choose the “De novo assembly and contigs classification” sample.
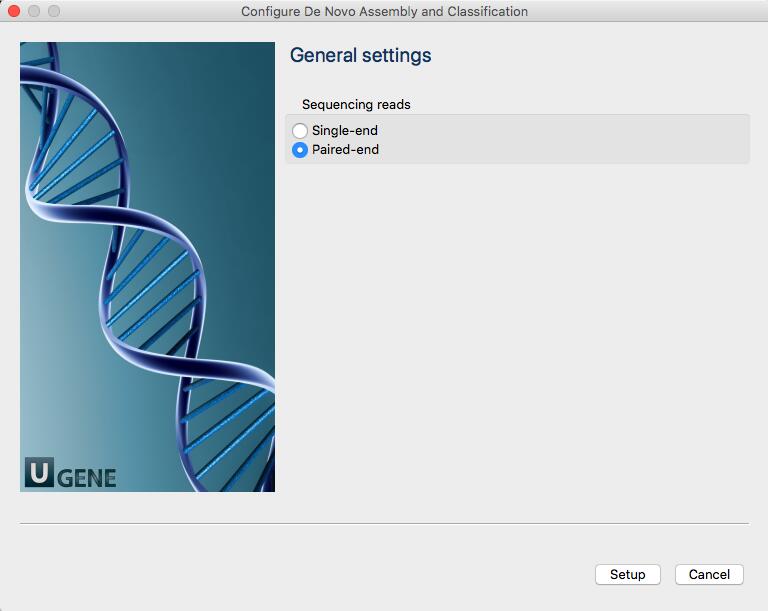
Once you double click on the window to start the analysis, a new window will open that will ask you whether your reads are single or paired.
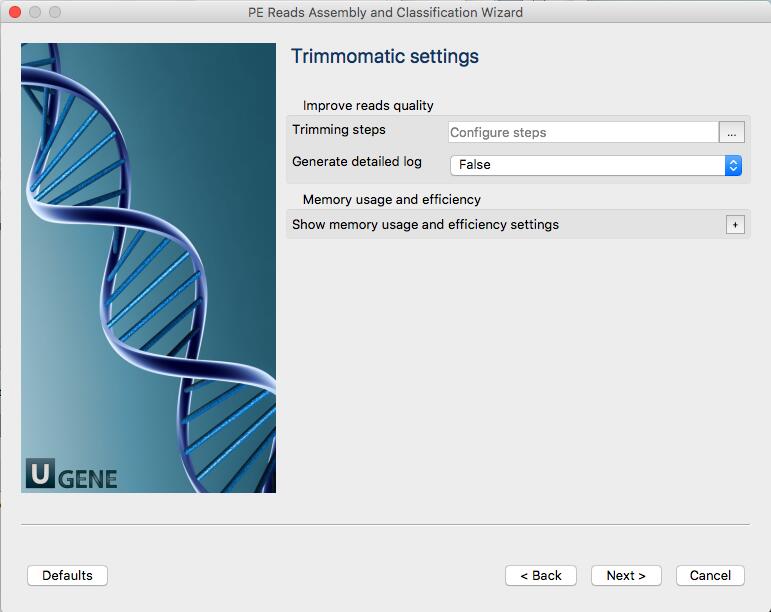
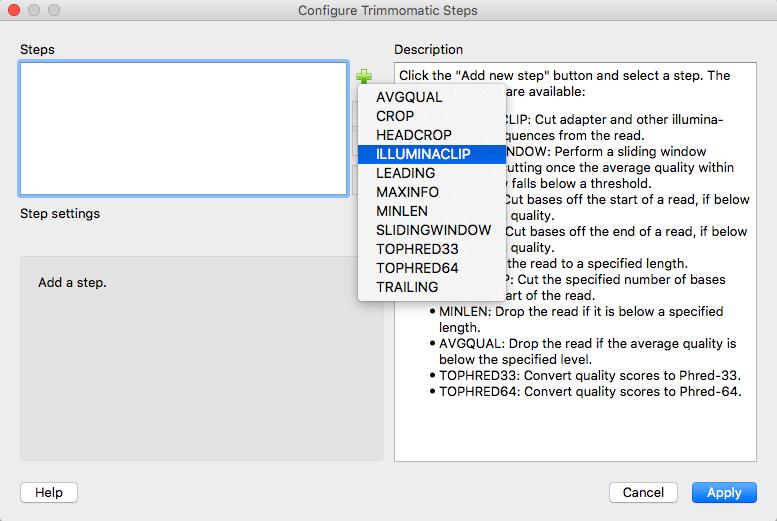
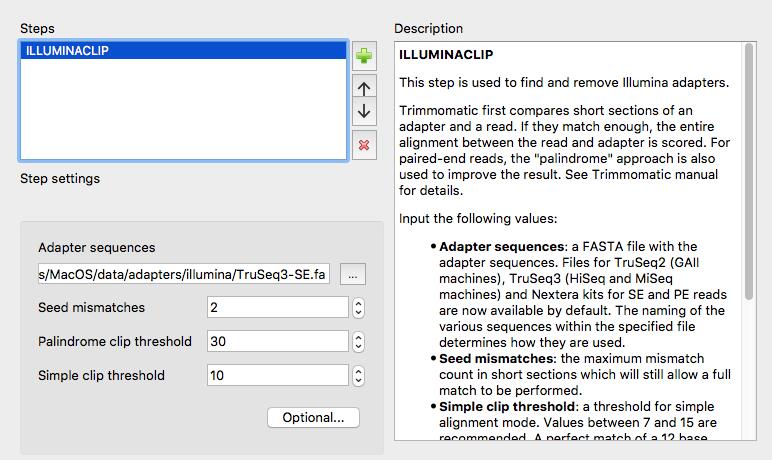
More information about Trimmomatic: http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic
For single-ended data, one input and one output file are specified, plus the processing steps. For paired-end data, two input files are specified, and 4 output files, 2 for the ‘paired’ output where both reads survived the processing, and 2 for corresponding ‘unpaired’ output where a read survived, but the paired read did not.
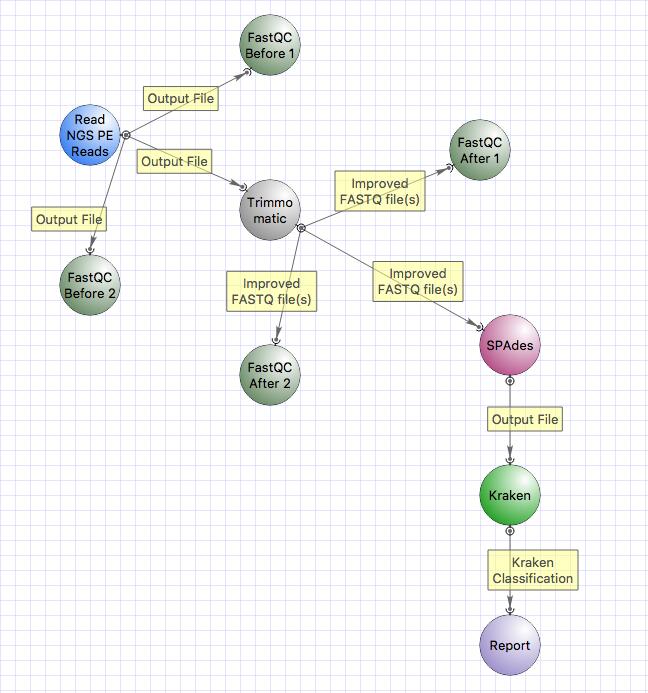
The workflow that you have generated contains SPAdes, but in this practical session we will not use SPAdes prior classification with Kraken.
Now we will remove SPAdes and connect the output of Trimmomatic directly to Kraken input.
To remove SPAdes click on the element and with the right click choose “Delete”.
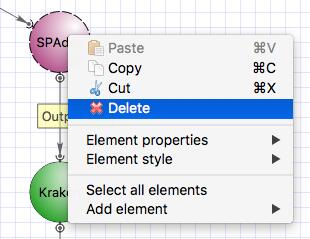
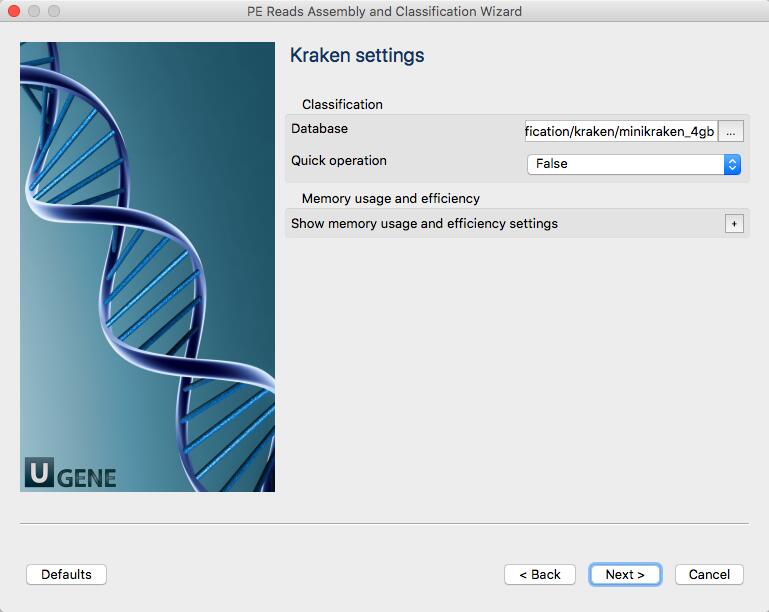
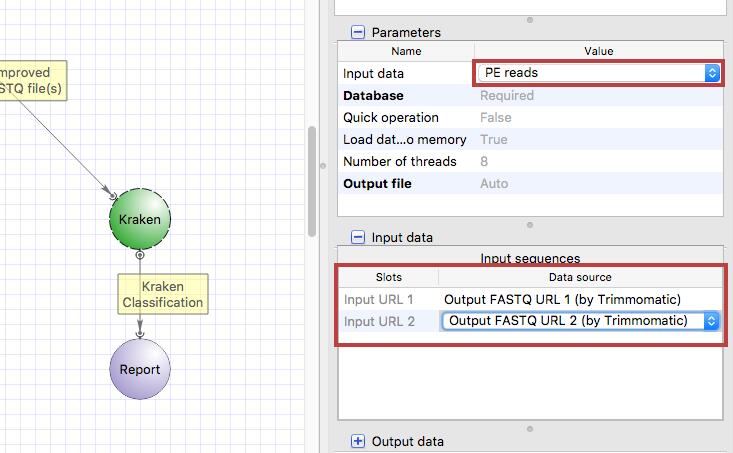
Select the Kraken input port, press Alt on the keyboard and move the port up. Then drag an arrow from Trimmomatic output port to Kraken input port. Clik on the Kraken element and configure the “Input data” parameter and input slots.
Click  on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
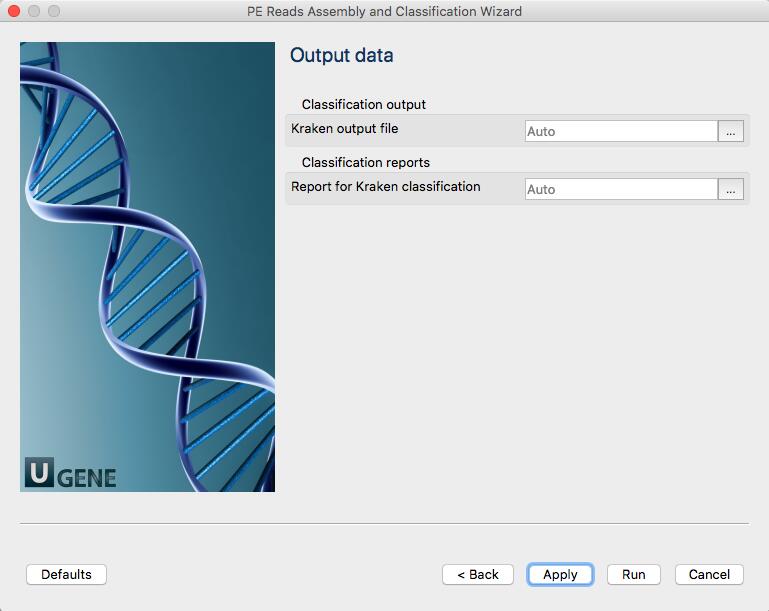
The workflow outputs two files:
- lib3.R1_001_Kraken_classification.txt: output by Kraken contains classification of with each NGS read,
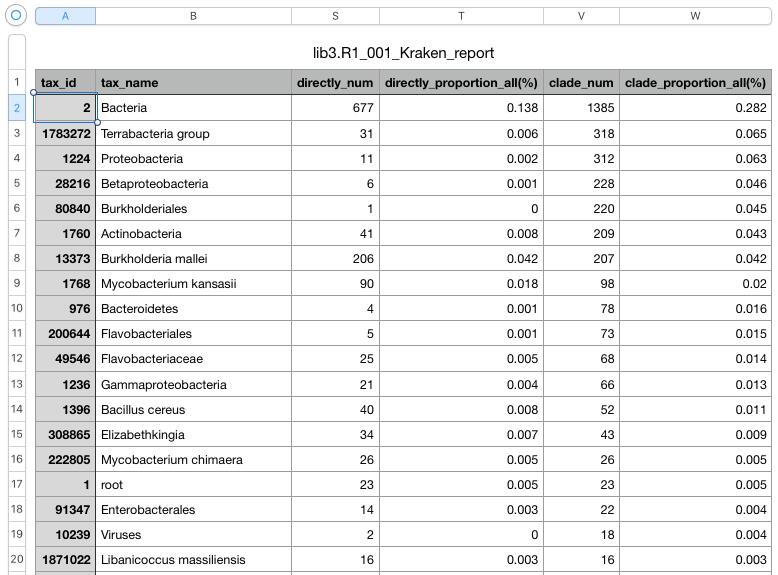
- lib3.R1_001_Kraken_report.txt: a report file, generated by UGENE, with general statistics per each taxID.
The second file is a tab-delimited text file. Open it in a Excel-like application. For each taxID the file contains, in particular, the following information:
- tax_name: scientific name, associated with the taxID;
- directly_num: number of NGS reads, directly assigned to the taxID;
- clade_num: number of NGS reads, assigned to this taxID or one of the children in the taxonomy tree (e.g. “clade_num” for “tax_id = 2” will include the number of all bacterial reads).
Exercises
Exercise: Repeat taxonomical classification workflow with lib5 data. Compare the results.
Exercise: Classify reads with the default workflow using SPAdes and Kraken. Compare the results
What’s next?
MiniKraken is a rather small pre-build database. You can build a custom database with “Build Kraken Database” element and use this database instead of MiniKraken.
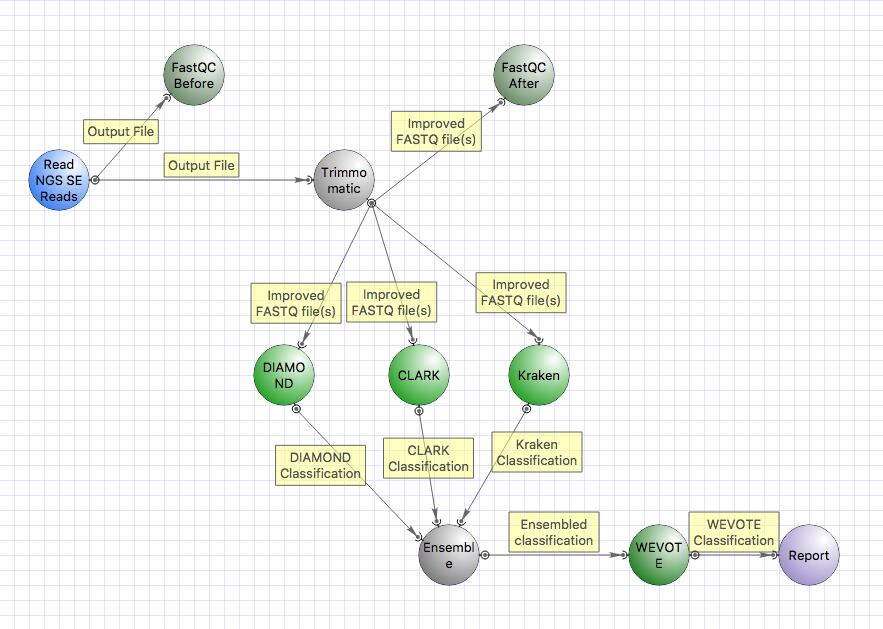
You can also use the parallel and serial taxonomical classification workflows with additional classifiers CLARK, DIAMOND and WEVOTE. Note that this requires more disk space (full UGENE package with metagenomics data takes ~ 250Gb). More advanced computational resources (RAM etc.) are also needed.
Acknowledgement
This tutorial is an adapted version of the tutorial by Carla Mavian, prepared for metagenomics practical session on VEME 2018 (see here).
The metagenomics framework in UGENE was supported by the VIROGENESIS project.

